Bilateral Filtering for Gray and Color Images
双边滤波器:保留边界的平滑滤波器。 在局部上,就是在灰度值差异不大的区域平滑,在灰度值差异比较大的边界地区保留边界。所以双边滤波器作用于每个像素的同时,必然会受到领域像素点的距离、灰度值差的权重影响。
已知低通滤波可以表示为:
range filter可以表示为:(range filter 试选定一个数值范围,再做滤波的一个操作)
所以,双边滤波器的定义是:
其中,kx)是归一化(normalize)函数,
( f 表示原图像,h 表示处理后的图像 x 表示 h 中某个像素点位置,ξ 表示 f 中x位置像素点的邻域像素,fξ)表示该像素点的灰度值,c表示低通滤波, s表示range filter)
其中,
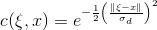

//Filters.h #ifndef FILTERS_H #define FILTERS_H #include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" #include "opencv2/core.hpp" #include <iostream> #include <cmath> //Bilateral Filtering //sigmaD == sigmaSpace, sigmaR == sigmaColor cv::Mat BilateralFiltercv::Mat inputImg, int filterSize, double sigmaD, double sigmaR); cv::Mat fastBilateralFiltercv::Mat inputImg, int filterSize, double sigmaD, double sigmaR); #endif // ! FILTERS_H
//Filters.cpp #include "Filters.h" double SpaceFactorint x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, double sigmaD) { double absX = powabsx1 - x2), 2); double absY = powabsy1 - y2), 2); return exp-absX + absY) / 2 * powsigmaD, 2))); } double ColorFactorint x, int y, double sigmaR) { double distance = absx - y) / sigmaR; return exp-0.5 * powdistance, 2)); } cv::Mat BilateralFiltercv::Mat inputImg, int filterSize, double sigmaD, double sigmaR) { int len; //must be odd number cv::Mat gray; // must be 1-channel image cv::Mat LabImage; // if channels == 3 if filterSize % 2 != 1 || filterSize <= 0) { std::cerr << "Filter Size must be a positive odd number!" << std::endl; return inputImg; } len = filterSize / 2; if inputImg.channels) >= 3) { cv::cvtColorinputImg, LabImage, cv::COLOR_BGR2Lab); gray = cv::Mat::zerosLabImage.size), CV_8UC1); for int i = 0; i < LabImage.rows; i++) { for int j = 0; j < LabImage.cols; j++) { gray.ptr<uchar>i)[j] = LabImage.ptr<uchar>i, j)[0]; } } } else ifinputImg.channels) == 1){ inputImg.copyTogray); } else { std::cerr << "the count of input image's channel can not be 2!" << std::endl; return inputImg; } cv::Mat resultGrayImg = cv::Mat::zerosgray.size), CV_8UC1); for int i = 0; i < gray.rows; i++) { for int j = 0; j < gray.cols; j++) { double k = 0; double f = 0; for int r = i - len; r <= i + len; r++) { for int c = j - len; c <= j + len; c++) { if r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= gray.rows || c >= gray.cols) continue; f = f + gray.ptr<uchar>r)[c] * SpaceFactori, j, r, c, sigmaD) * ColorFactorgray.ptr<uchar>i)[j], gray.ptr<uchar>r)[c], sigmaD); k += SpaceFactori, j, r, c, sigmaD) * ColorFactorgray.ptr<uchar>i)[j], gray.ptr<uchar>r)[c], sigmaD); } } int value = f / k; if value < 0) value = 0; else if value > 255) value = 255; resultGrayImg.ptr<uchar>i)[j] = uchar)value; } } cv::Mat resultImg; if inputImg.channels) >= 3) { for int i = 0; i < LabImage.rows; i++) { for int j = 0; j < LabImage.cols; j++) { LabImage.ptr<uchar>i, j)[0] = resultGrayImg.ptr<uchar>i)[j]; } } cv::cvtColorLabImage, resultImg, cv::COLOR_Lab2BGR); } else { resultGrayImg.copyToresultImg); } return resultImg; } cv::Mat fastBilateralFiltercv::Mat inputImg, int filterSize, double sigmaD, double sigmaR) { int len; //must be odd number cv::Mat gray; // must be 1-channel image cv::Mat LabImage; // if channels == 3 if filterSize % 2 != 1 || filterSize <= 0) { std::cerr << "Filter Size must be a positive odd number!" << std::endl; return inputImg; } len = filterSize / 2; if inputImg.channels) >= 3) { cv::cvtColorinputImg, LabImage, cv::COLOR_BGR2Lab); gray = cv::Mat::zerosLabImage.size), CV_8UC1); for int i = 0; i < LabImage.rows; i++) { for int j = 0; j < LabImage.cols; j++) { gray.ptr<uchar>i)[j] = LabImage.ptr<uchar>i, j)[0]; } } } else if inputImg.channels) == 1) { inputImg.copyTogray); } else { std::cerr << "the count of input image's channel can not be 2!" << std::endl; return inputImg; } cv::Mat resultGrayImg = cv::Mat::zerosgray.size), CV_8UC1); for int i = 0; i < gray.rows; i++) { for int j = 0; j < gray.cols; j++) { double k = 0; double f = 0; double sum = 0; for int r = i - len; r <= i + len; r++) { if r < 0 || r >= gray.rows) continue; f = f + gray.ptr<uchar>r)[j] * SpaceFactori, j, r, j, sigmaD) * ColorFactorgray.ptr<uchar>i)[j], gray.ptr<uchar>r)[j], sigmaD); k += SpaceFactori, j, r, j, sigmaD) * ColorFactorgray.ptr<uchar>i)[j], gray.ptr<uchar>r)[j], sigmaD); } sum = f / k; f = k = 0.0; for int c = j - len; c <= j + len; c++) { if c < 0 || c >= gray.cols) continue; f = f + gray.ptr<uchar>i)[c] * SpaceFactori, j, i, c, sigmaD) * ColorFactorgray.ptr<uchar>i)[j], gray.ptr<uchar>i)[c], sigmaD); k += SpaceFactori, j, i, c, sigmaD) * ColorFactorgray.ptr<uchar>i)[j], gray.ptr<uchar>i)[c], sigmaD); } int value = sum + f / k) / 2; if value < 0) value = 0; else if value > 255) value = 255; resultGrayImg.ptr<uchar>i)[j] = uchar)value; } } cv::Mat resultImg; if inputImg.channels) >= 3) { for int i = 0; i < LabImage.rows; i++) { for int j = 0; j < LabImage.cols; j++) { LabImage.ptr<uchar>i, j)[0] = resultGrayImg.ptr<uchar>i)[j]; } } cv::cvtColorLabImage, resultImg, cv::COLOR_Lab2BGR); } else { resultGrayImg.copyToresultImg); } return resultImg; }
//main.cpp #include <iostream> #include <time.h> #include "Filters.h" using namespace std; int main) { cv::Mat img = cv::imread"Capture.jpg", cv::IMREAD_UNCHANGED); clock_t begin_time = clock); cv::Mat result = BilateralFilterimg, 15, 12.5, 50); std::cout << floatclock) - begin_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std:: endl; cv::imshow"original", result); cv::waitKey0); cv::imwrite"original.jpg", result); begin_time = clock); result = fastBilateralFilterimg, 15, 12.5, 50); std::cout << floatclock) - begin_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; cv::imshow"fast", result); cv::waitKey0); cv::imwrite"fast.jpg", result); begin_time = clock); cv::bilateralFilterimg, result, 15, 50, 12.5); std::cout << floatclock) - begin_time) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << std::endl; cv::imshow"opencv", result); cv::waitKey0); cv::imwrite"opencv.jpg", result); system"pause"); return 0; }
运行结果:
46.889s 5.694s 0.202s
二维算子降成两个一维算子之后,速度加快了一些,但是还是不如opencv的快,效果也比它差一些No more reinventing the wheel…)
从左至右:“小雀斑”帅气原图、BilateralFilter处理结果、fastBilateralFilter处理结果、opencv接口处理结果





